Plants are highly dependent on light for their growth and survival. While the visible spectrum of light is essential for photosynthesis, ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) light also play important roles in plant physiology.
UV light, for instance, can stimulate the production of secondary metabolites in plants, which can improve their resistance to pests and diseases. IR light, on the other hand, can trigger changes in plant morphology and development, such as the elongation of stems and leaves. In recent years, the use of harmful UV and IR light in grow environments has become increasingly popular among plant growers, particularly for cultivating crops like cannabis plants.
In this article, we will explore the impact of UV light and IR light on plant growth and development, and discuss some of the most commonly asked questions about these types of light in a grow environment.
Basic Knowledge of UV and IR Light
What Is UV Light?
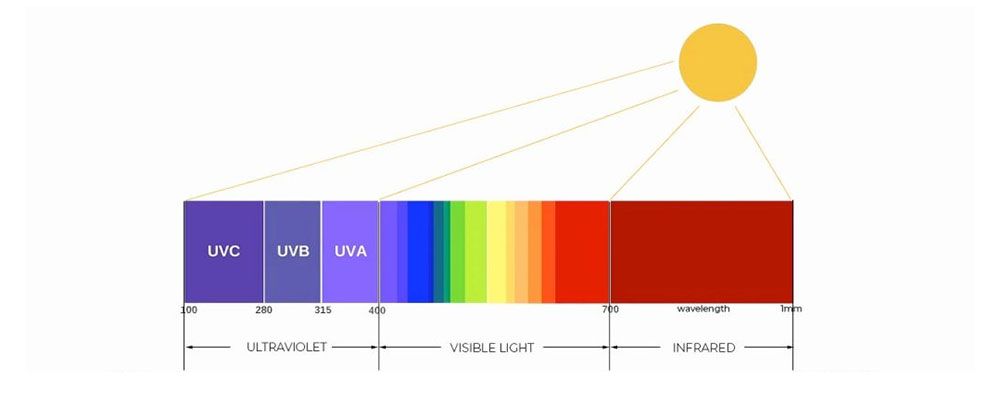
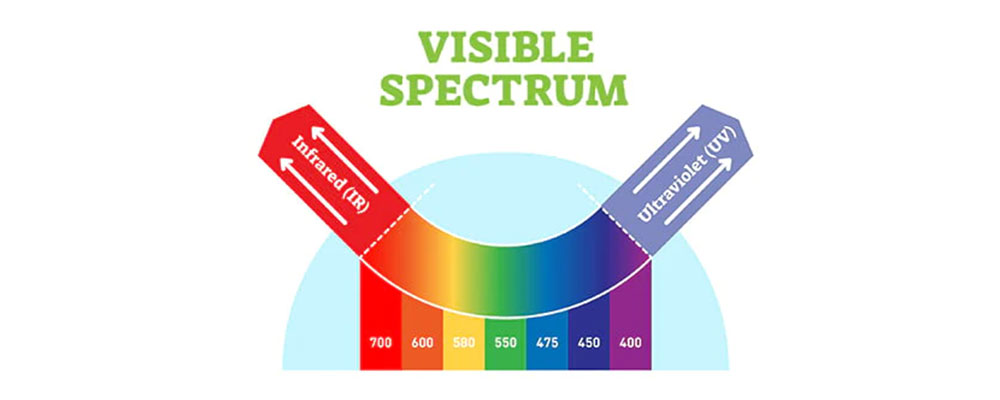
Ultraviolet (UV) light and infrared (IR) light are two types of electromagnetic radiation that are not visible to the human eye. The UV spectrum wavelengths is shorter than visible light, and is categorized into three main subtypes: UV-A, UV-B, and UV-C.
UV-A light has a longer wavelength(about 400nm-315nm) and lower energy than UV-B and UV C, and can penetrate deeper into plant tissues. It is often referred to as “black light” and is commonly used in horticulture to stimulate plant growth and improve the quality of flowers and fruits.
UV-B light has a shorter wavelength(about 315nm-280nm) and higher energy than UV-A, and can cause damage to plant DNA and proteins if exposure is prolonged. However, it is also an important trigger for the production of secondary metabolites, such as flavonoids and anthocyanins, which can enhance plant resistance to pests and diseases.
UV-C light has the shortest wavelength(about 280nm-100nm) and highest energy of the three subtypes, and is the most harmful to living organisms. It is typically filtered out by the earth’s atmosphere, but can be generated artificially and used to sterilize growing media and equipment in a grow environment.
What Is IR Light?
Infrared (IR) light is a type of electromagnetic radiation that has a longer wavelength than visible light(more than 700nm), and is not visible to the human eye. IR radiation is divided into three main subtypes based on their wavelength: near-infrared (NIR), mid-infrared (MIR), and far-infrared (FIR). NIR radiation has the shortest wavelength and is closest in wavelength to visible light, while MIR and FIR have longer wavelengths and are often used in heating applications. IR radiation is an important part of the electromagnetic spectrum, and can have both beneficial and harmful effects on living organisms, including plants.
The Impact of Ultraviolet Light on Plants
Ultraviolet (UV) light has been shown to have a significant impact on plant growth and development. While prolonged exposure to high levels of UV radiation can be harmful to plants, controlled exposure to moderate levels of UV light radiation can have beneficial effects.
UV light radiation is an important environmental factor that can regulate plant growth and development through various mechanisms. One of the most well-studied effects of UV light radiation on plants is the induction of secondary metabolites, such as flavonoids, phenolics, and carotenoids. These compounds play important roles in plant defense against biotic and abiotic stressors, as well as in plant signaling and reproduction. UV light radiation has also been shown to affect plant morphology, including leaf thickness, plant height, and branching patterns.
In addition, UV radiation can influence plant photosynthesis and carbon assimilation, which can affect plant biomass accumulation and yield. Overall, the impact of UV light radiation on plant growth and development is complex and multifaceted, and varies depending on the wavelength, intensity, and duration of exposure.
The Impact of Infrared Light on Plants
Infrared (IR) radiation, particularly the near-infrared (NIR) range, has been shown to have beneficial effects on plant growth and development. NIR radiation can penetrate plant tissues more deeply than visible light, allowing it to stimulate cellular activity and photosynthesis in the lower layers of leaves and stems. This can lead to increased plant growth, improved biomass accumulation, and enhanced crop yields.
In addition, NIR radiation has been shown to improve plant water use efficiency, by increasing the expression of aquaporin genes and reducing transpiration rates. This can help plants to conserve water and survive under water-limited conditions.

The Drawbacks of UV and IR Light
Although UV and IR lights are beneficial to plants’ growth, excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) light can also have negative effects on plants. Overexposure to UV light for plants can cause damage to plant cells, including the breaking down of chlorophyll, which is essential for photosynthesis. This can result in stunted growth, reduced yields, and even death of the plant. Prolonged exposure to UV light for plants can also cause leaves to become brittle and discolored.
Similarly, excessive exposure to IR light can also be harmful to plants. While plants require some amount of IR light for optimal growth and development, excessive exposure can lead to heat stress and dehydration, which can cause the plant to wilt or die. In addition, IR light can also cause the leaves of some plants to become scorched or discolored, affecting their ability to perform photosynthesis.
How Can I Apply UV&IR into My Growing?

UV (ultraviolet) and IR (infrared) light can be used to improve the growth and health of plants in a variety of growing settings, including indoor and outdoor gardens, hydroponic setups, and greenhouses. To apply UV and IR into your growing process, you will need to follow these steps:
- Seedling stage: During the early stages of plant growth, exposure to UV light can help stimulate plant growth and improve resistance to pests and diseases. To apply UV light for plants during the seedling stage, use a specialized grow light that emits UV radiation light and position it 6 to 12 inches above the seedlings. Keep the UV lighting on for 2-4 hours per day.
- Vegetative stage: During the vegetative stage, plants need a lot of light to support photosynthesis and growth. IR light can help promote stem and leaf growth, so it’s recommended to use a grow light that emits both UV and IR light. Position the light 12 to 18 inches above the plants and keep it on for 16 to 18 hours per day.
- Flowering stage: During the flowering stage, plants need a specific light spectrum to support the development of buds and flowers. It’s recommended to use a grow light bar that emits both UV and IR light, along with blue and red light. Position the light 18 to 24 inches above the plants and keep it on for 12 hours per day.
In addition to the above suggestions about using UV&IR in the complete growing process, there are some other tips for you:
- Determine the appropriate type and intensity of UV and IR light for your plants. Different plants have varying needs and tolerance for these types of light, so it’s important to research and understand the specific requirements for your plants.
- Choose the appropriate UV and IR light source. You can purchase specialized grow lights that emit UV and IR light or use natural sunlight, which also contains both types of radiation.
- Position the light source correctly. Make sure that your plants receive the appropriate amount of UV and IR light by positioning the light source at the correct distance and angle. Consult your light source’s instructions for optimal positioning.
- Set a timer for the UV and IR light. Depending on the type of plant, UV and IR light exposure can range from several minutes to several hours per day. Consult plant-specific guides for recommended exposure times.
- Monitor your plants regularly for signs of stress or damage. While UV and IR light can be beneficial for plant growth, it can also be harmful if used improperly. Be sure to follow all safety guidelines and best practices for using these types of lights.
Use Mars Hydro UR45 LED Grow Light to Supply UV and IR Light for Your Plants
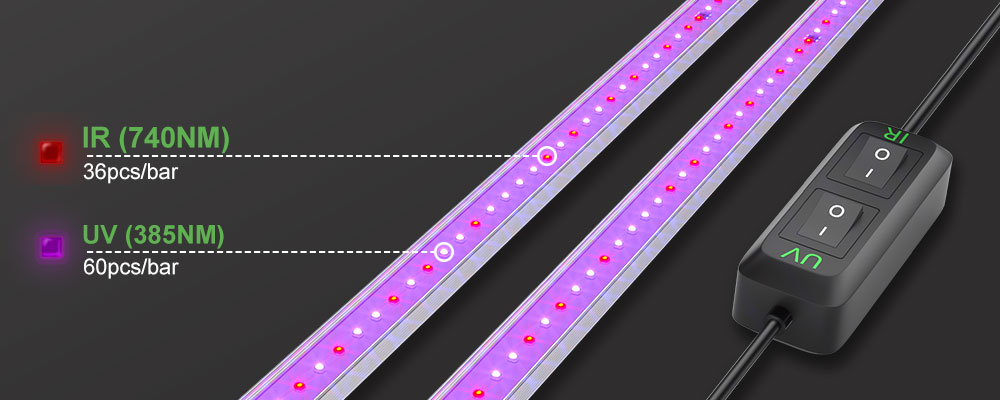
Mars Hydro UR45 LED grow lightwith UV and IR light is an excellent option for growers who want to provide their plants with a balanced spectrum of light, including UV and IR wavelengths. This grow light bar is equipped with 45 high-quality LED chips, including 4 IR and 2 UV chips, which provide a full spectrum of light that is essential for plant growth and development.
The UV light cultivation for plants helps to stimulate the production of secondary metabolites in plants, which can improve the plant’s overall health and resilience to pests and diseases. The IR light, on the other hand, helps to promote cell division and elongation, which is crucial for healthy plant growth.
Additionally, this grow light is designed to be energy-efficient, consuming only 100 watts of power, while still providing high-quality light that can support plant growth throughout their entire life cycle.
Overall, the Mars Hydro UR45 LED grow light with UV and IR light is an excellent investment for growers who want to provide their plants with the full temperature and full spectrum of light they need to thrive.
To help growers better understand UV&IR light and Mars Hydro UR45 LED Grow Light, there is a detailed video for your reference:
At last, if you have any other questions about Mars Hydro UR45 LED grow lights for UV and IR supplement or other products, please feel free to contact us. Mars Hydro will always provide the most professional growing equipment and growing guides for you!